Code
library(tidyverse)Robyn Steveley
February 11, 2024
The Data sets being used:
Figure 1
Figure 2
#fig 3
fig_3 <- ggplot(BOOKS, aes(pages))+ geom_histogram(binwidth = 20, color="blue", fill="blue")
#Style
fig_3_titles <- labs(title = "Figure 1: Number of Pages for Top 100 Young Adult Books",
caption = "This graph shows the number of pages of the most popular young adult books to within 20 pages.")
fig_3_theme <- theme(panel.background=element_rect(fill="white"),
plot.caption = element_text(hjust = 0.5))
#Showing figure 4
fig_3 <- fig_3 + fig_3_titles + fig_3_theme
print(fig_3)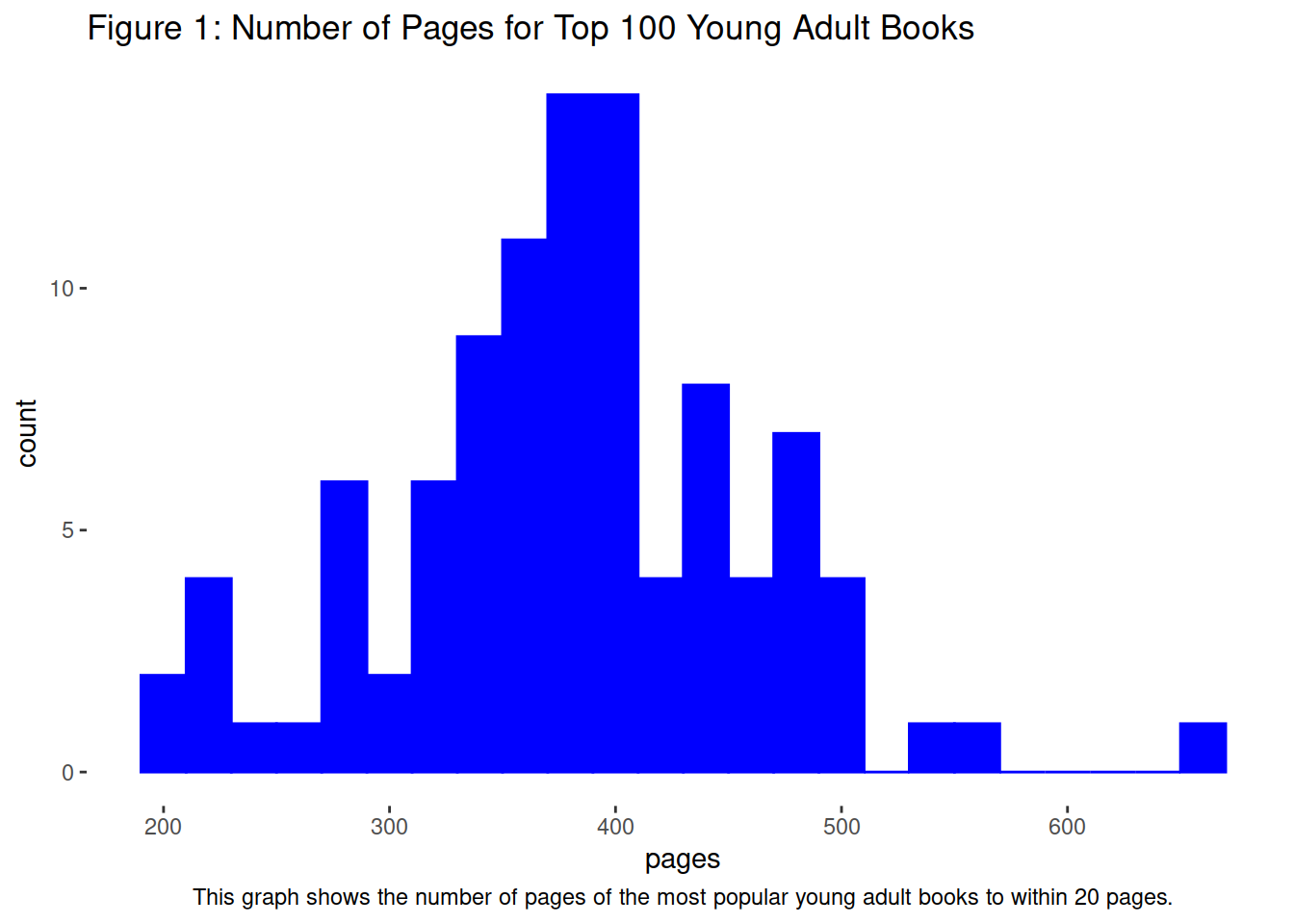
#fig 4
fig_4 <- ggplot(BOOKS, aes(pages))+ geom_histogram(binwidth = .5, color="red", fill="red")
#Style
fig_4_titles <- labs(title = "Figure 2: Number of Pages for Top 100 Young Adults Books",
caption = "This uses bin sizes of half a page. The data doesn't even measure book length to half pages.")
fig_4_theme <- theme(panel.background=element_rect(fill="white"),
plot.caption = element_text(hjust = 0.5))
#Showing figure 4
fig_4 <- fig_4 + fig_4_titles + fig_4_theme
print(fig_4)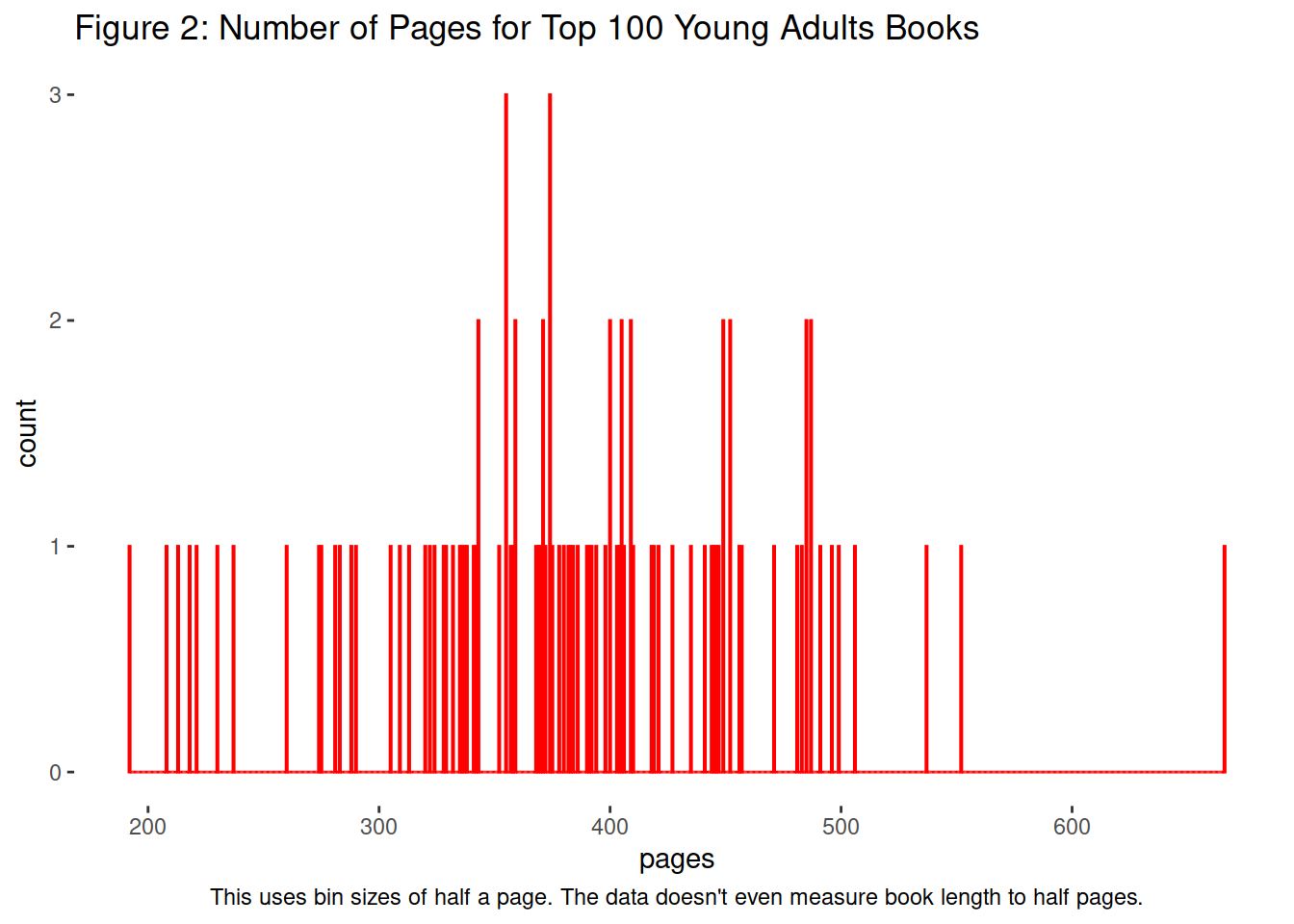
Figure 5
# a graph that uses a two or more channels to encode two or more attributes while maintaining separability.
MOVIES_3 <- MOVIES %>%
filter(grepl("Pixar", production_companies)) %>%
filter(runtime > 40) %>%
filter(runtime < 140) %>%
filter(budget > 0)
#filter these down to something interesting. only a couple of movies or only movies from a certain genre or country
ggplot(MOVIES_3, aes(x = reorder(title, +budget), y = runtime, fill = budget)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity") +
coord_flip() +
labs(title = "Pixar Movies",
x = "Movies",
y = "Runtime (minutes)") +
geom_text(aes(label = budget/1e6), hjust = +1, color = "lightyellow") +
theme(panel.background = element_rect(fill = "grey"),
panel.grid = element_blank(),
axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 90, hjust = 0),
plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.1))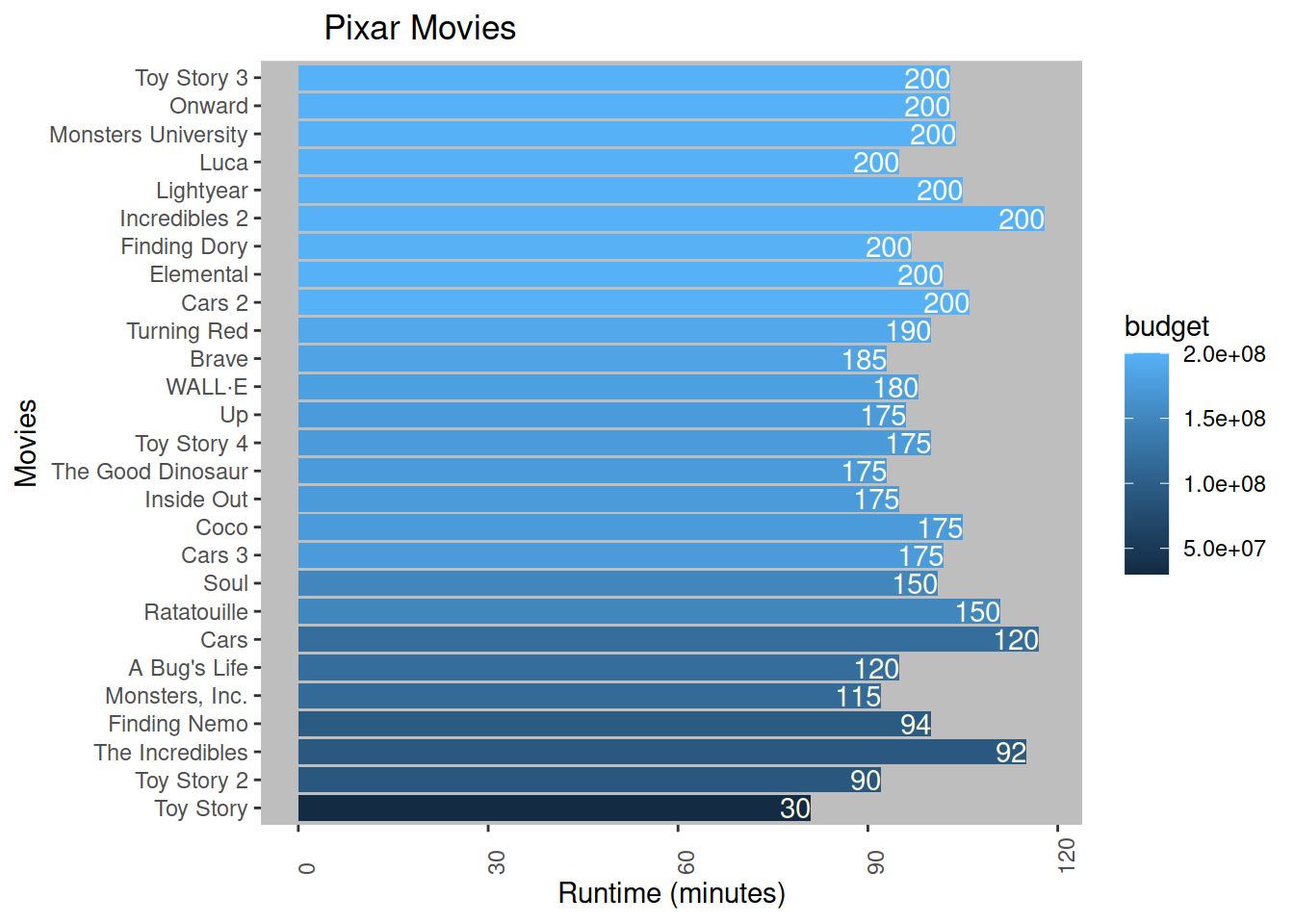
Figure 6
# a graph that uses a two or more channels to encode two or more attributes while and confuses separability.
ggplot(MOVIES_3, aes(x = title, y = runtime, fill = budget)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity") +
coord_flip() +
labs(title = "Pixar Movies",
x = "Movies",
y = "runtime") +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 90, hjust = 1),
plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.1))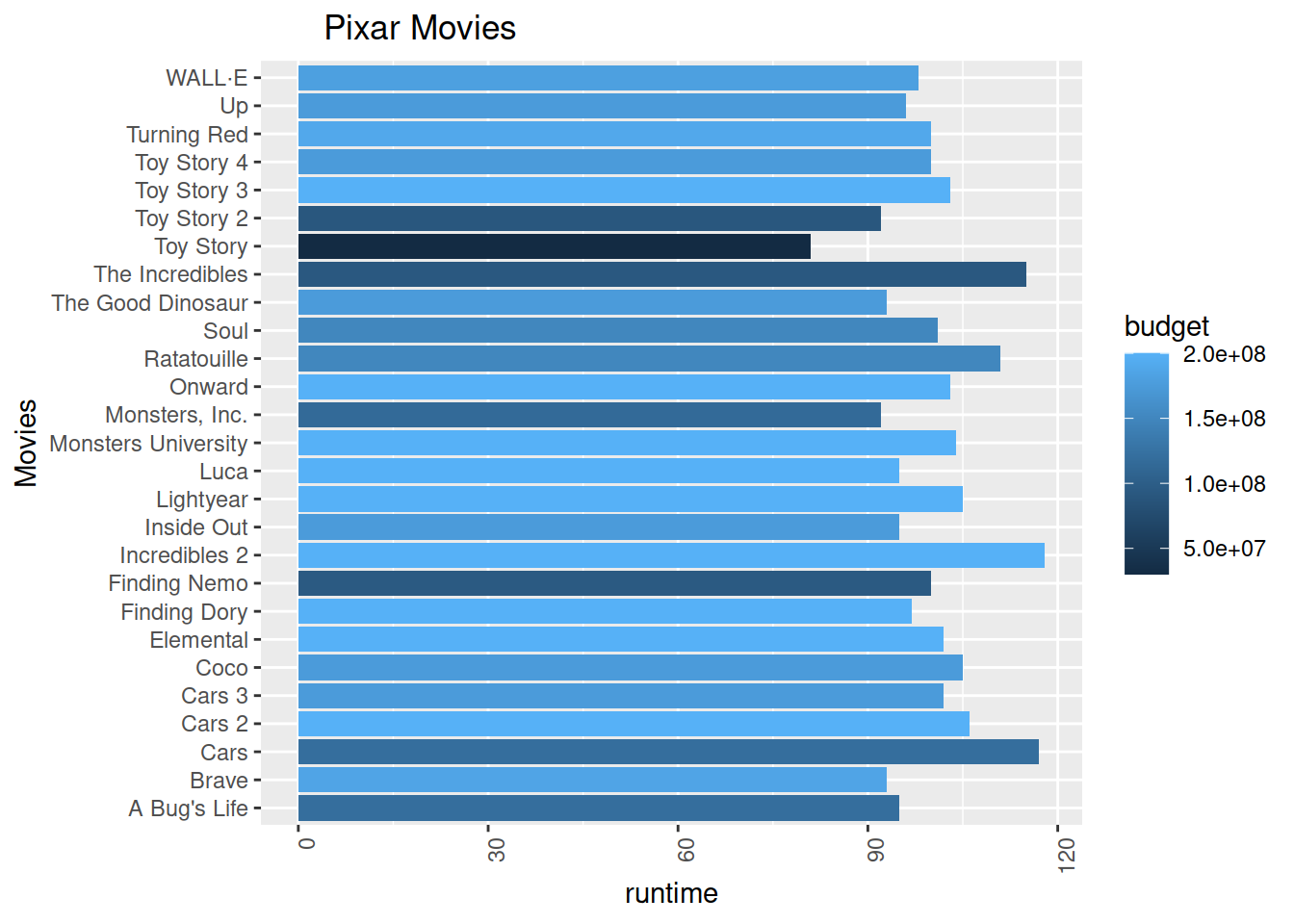
Figure 7
Figure 8
---
title: "Assignment 4"
subtitle: "Marks and Channels"
author: "Robyn Steveley"
date: "2024-02-11"
categories: [assignment]
image: "books_picture_Nick_Fewings.jpg"
code-fold: true
code-tools: true
description: "In progress..."
---
# Marks and Channels
```{r}
#| output: false
library(tidyverse)
```
The Data sets being used:
[Top 100 Young Adult Books](https://data.world/yansian/top-100-young-adult-fiction)
[52,000 Animated Movies](https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/asaniczka/52000-animation-movie-details-dataset-2024)
```{r}
BOOKS <- read.csv("goodreads_Top100_YoungAdultFiction1.csv")
MOVIES <- read.csv("Animation_Movies.csv")
```
## Expressiveness and Effectiveness
Figure 1
```{r}
# a graph that shows the relationship between ordered data clearly and does not imply an ordering where there is none.
```
Figure 2
```{r}
# a graph that messes up the relationship between ordered data and unordered data. The relationship of the order is confusing and possibly relationship are implied that don't exist.
```
## Discriminability
```{r}
#fig 3
fig_3 <- ggplot(BOOKS, aes(pages))+ geom_histogram(binwidth = 20, color="blue", fill="blue")
#Style
fig_3_titles <- labs(title = "Figure 1: Number of Pages for Top 100 Young Adult Books",
caption = "This graph shows the number of pages of the most popular young adult books to within 20 pages.")
fig_3_theme <- theme(panel.background=element_rect(fill="white"),
plot.caption = element_text(hjust = 0.5))
#Showing figure 4
fig_3 <- fig_3 + fig_3_titles + fig_3_theme
print(fig_3)
```
```{r}
#fig 4
fig_4 <- ggplot(BOOKS, aes(pages))+ geom_histogram(binwidth = .5, color="red", fill="red")
#Style
fig_4_titles <- labs(title = "Figure 2: Number of Pages for Top 100 Young Adults Books",
caption = "This uses bin sizes of half a page. The data doesn't even measure book length to half pages.")
fig_4_theme <- theme(panel.background=element_rect(fill="white"),
plot.caption = element_text(hjust = 0.5))
#Showing figure 4
fig_4 <- fig_4 + fig_4_titles + fig_4_theme
print(fig_4)
```
## Separability
Figure 5
```{r}
# a graph that uses a two or more channels to encode two or more attributes while maintaining separability.
MOVIES_3 <- MOVIES %>%
filter(grepl("Pixar", production_companies)) %>%
filter(runtime > 40) %>%
filter(runtime < 140) %>%
filter(budget > 0)
#filter these down to something interesting. only a couple of movies or only movies from a certain genre or country
ggplot(MOVIES_3, aes(x = reorder(title, +budget), y = runtime, fill = budget)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity") +
coord_flip() +
labs(title = "Pixar Movies",
x = "Movies",
y = "Runtime (minutes)") +
geom_text(aes(label = budget/1e6), hjust = +1, color = "lightyellow") +
theme(panel.background = element_rect(fill = "grey"),
panel.grid = element_blank(),
axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 90, hjust = 0),
plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.1))
```
Figure 6
```{r}
# a graph that uses a two or more channels to encode two or more attributes while and confuses separability.
ggplot(MOVIES_3, aes(x = title, y = runtime, fill = budget)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity") +
coord_flip() +
labs(title = "Pixar Movies",
x = "Movies",
y = "runtime") +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 90, hjust = 1),
plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.1))
```
## Popout
Figure 7
```{r}
# a graph where popout is used
```
Figure 8
```{r}
# a graph where popout is not used
```